Describe What Happens When a Muscle Contracts.
This makes the sarcomeres shorter and thicker contracting the muscle. Cardiac Muscle Contraction The sarcolemma plasma membrane of an unstimulated muscle cell is polarizedthat is the inside of the sarcolemma is negatively charged with respect to the outside.
Muscle Contractions Learn Muscular Anatomy
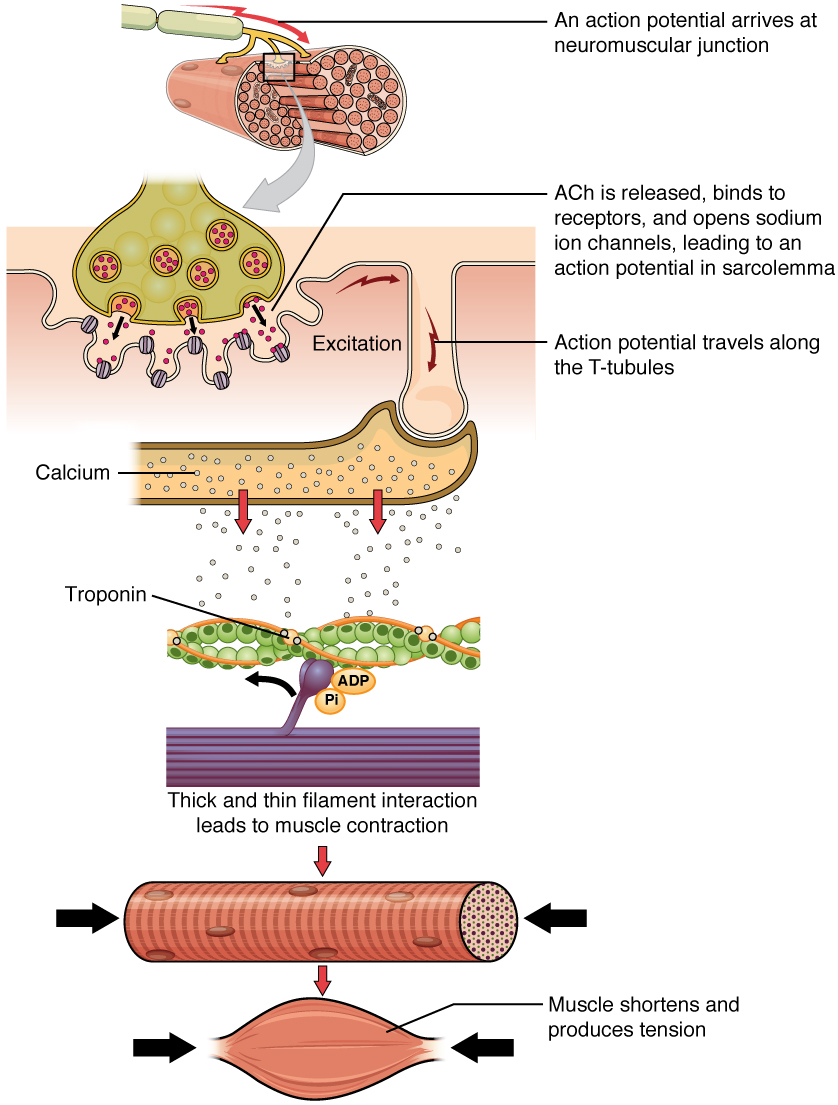
Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal.

. Generally when a muscle contracts small motor units will be the first ones recruited in a muscle with larger motor units added as more force is needed. When the muscle starts to contract and needs energy creatine phosphate transfers its phosphate back to ADP to form ATP and creatine. Thus creatine phosphate-derived ATP powers the first few seconds of muscle contraction.
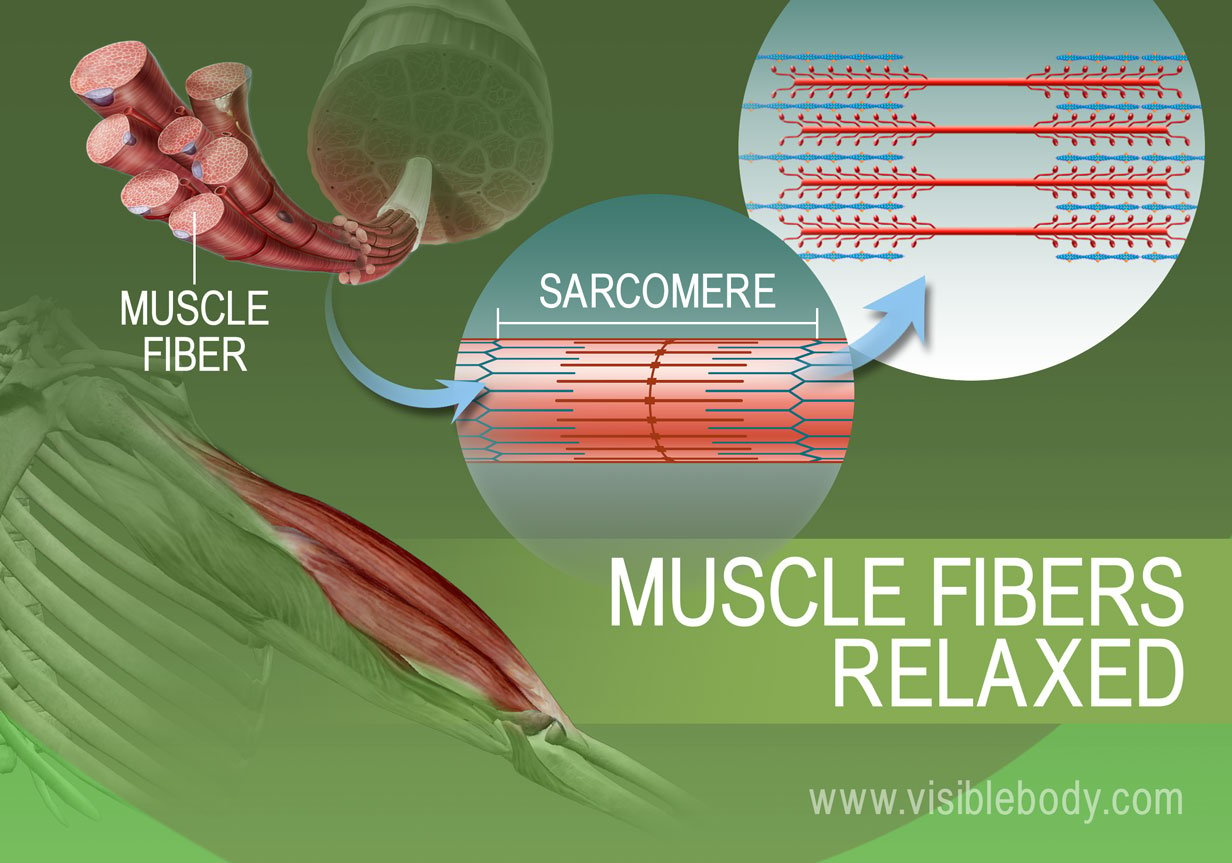
During a muscle contraction every sarcomere will shorten 1 bringing the Z-lines closer together 2. When a muscle contracts the actin is pulled along myosin toward the center of the sarcomere until the actin and myosin filaments are completely overlapped. The primary mode of action for muscle is by contraction.
Thus creatine phosphate-derived ATP powers the first few seconds of muscle contraction. For a skeletal muscle fiber to contract its membrane must first be excitedin other words it must be stimulated to fire an action potential. The actin and myosin cross bridges bind and.
This is the power stroke. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme creatine kinase and occurs very quickly. In order to contract a muscle the first thing that needs to occur is that there must be an influx of calcium ions.
Although the term excitation-contraction coupling confuses or scares some students it comes down to this. Thus the excitation-contraction coupling process begins with signaling from the nervous system at the neuromuscular junction Figure 1031 and ends with calcium release for muscle contraction. The Sliding Filament Theory of Muscles.
This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme creatine kinase and occurs very quickly. Over time as muscle damage accumulates muscle mass is lost and greater functional impairments develop. Myosin head groups attach to the surrounding actin filaments forming a cross-bridge.
The motor nerve stimulates an action potential impulse to pass down a neuron to the neuromuscular junction. 2 A motor neuron in the ventral horn of the spinal cord is activated and an action potential passes outward in a ventral root of the spinal. When a sarcomere shortens some regions shorten whereas others stay the same length.
At the NMJ the axon terminal releases ACh. The motor end-plate is the location of the ACh. The myofibrils shorten 3 too as does the whole muscle cell.
Without sufficient dystrophin muscle contractions cause the sarcolemma to tear causing an influx of Ca leading to cellular damage and muscle fiber degradation. The following steps are involved in muscle contraction. An action potential in a motor neuron causes acetylcholine to release in the synaptic cleft.
The signal an impulse called an action potential travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron. The primary function of a skeletal muscle is contraction and when a muscle contracts we produce an action preceded by an impulse from a nerve cell. Describe what is involved in muscle contraction.
This allows the tropomyosin to move. Sliding filament theory explains how the actin and myosin protein filaments create a muscle contraction. Figure 1031 Motor End-Plate and Innervation.
What are some misrepresentation of the human body. All of the motor units in a muscle can be active simultaneously producing a very powerful contraction. This stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium into the muscle cell.
Calcium floods into the muscle cell binding with troponin allowing actin and myosin to bind. 1 The sequence of events leading to contraction is initiated somewhere in the central nervous system either as voluntary activity from the brain or as reflex activity from the spinal cord. What happens on a microscopic level is that short.
What is the best approach to selecting safety equipment for an activity. Yet the myofilaments the thin and thick filaments do not get shorter 4. The muscle fiber action potential which sweeps along the sarcolemma as a wave is.
A Muscle Contraction Is Triggered When an Action Potential Travels Along the Nerves to the Muscles. Acetylcholine binds with receptors on the cell membrane on the muscle fiber opening Ca2 -Na channels. In other words for a muscle cell to contract the sarcomere must shorten.
The head group then bends causing the think filament to be pulled along and so overlap more with the thick filaments. This cannot last for very long because of the energy requirements of muscle contraction. During muscle contraction the actin filament is pulled along myosin toward the centre of the sarcomere until the actin and myosin filaments are completely overlapped.
What are the steps in muscle contraction. When the CNS sends a signal the thick and thin myosin filaments form a crossbridge pattern by sliding past each other. Muscle Contraction Steps in Detail.
When the muscle starts to contract and needs energy creatine phosphate transfers its phosphate back to ADP to form ATP and creatine. 1 Show answers Another question on Health. The unstimulated state of the muscle cell called the resting potential is created by the presence of large negatively charged proteins and nucleic acids inside the cell.
So lets do a quick review of muscle contraction physiology. It can happen when you hold or pick up something or. Muscle contraction is the tightening shortening or lengthening of muscles when you do some activity.
Describe what happens when a muscle contracts. This results in shortening of the sarcomere. When our skeletal muscles in our bodies contract they shorten by a process known as the Sliding Filament Theory proposed by Huxley in the 1960s.
A signal is sent from the brain or. These calcium ions cause the troponin that fixes the position of the tropomyosin to change shape.
13 1 Muscle Contraction Biology Libretexts

No comments for "Describe What Happens When a Muscle Contracts."
Post a Comment